This post is the latest in the FrontlineSMS Mobile Message series with National Geographic. To read a summary of the Mobile Message series click here.
By Florence Scialom, Community Support Coordinator, FrontlineSMS

"A group of Nigerian grassroots organizations and agencies have joined together to form ReclaimNaija, in an effort to provide the Nigerian electorate a way to report on the elections as they happen. ReclaimNaija documents how citizens are experiencing the elections by using FrontlineSMS to receive and send text message reports, and Ushahidi to visually map the election reports received. It is very exciting to see FrontlineSMS being used in this way, especially because one of the first public use cases of the software was during the last Nigerian elections in 2007. As Community Support Coordinator at FrontlineSMS I have had the privilege of speaking to Ngozi Iwere from Community Life Project, one of the promoters of ReclaimNaija, as well as others who have been involved in helping with and using the platform. I have learned about how Community Life Project are encouraging citizens from grassroots communities all over the country to use mobile technology to amplify the voice of Nigerian citizens, making their opinions impossible to ignore.
Amidst the confusion of date changes surrounding the Nigerian elections one thing remains clear; the people of Nigeria are ready to vote. The 2011 Nigerian elections got off to an uncertain start; with the National Assembly elections due on April 2nd 2011 having to be pushed back as a result of many problems, leading to the rescheduling of the whole two week election process. Amongst the commotion of date changes it is more important than ever for the Nigerian public to feel they have a way to speak out about any election problems they experience, and know they are being heard.
Over the years, elections in Nigeria have been surrounded by controversy. “Since the return to civil rule in 1999, all the elections conducted in Nigeria have been marred by massive fraud and violence,” says Ngozi Iwere.
It is clear speaking with Nigerian citizens about ReclaimNaija that people are keen to actively challenge the problems previously accompanying their elections. “On election days, citizens have been frustrated by a number of things; missing names, seeing ballot boxes stuffed or even stolen and other electoral fraud and yet being unable to do anything about this. This time however, is the time to speak out” says Femi Taiwo, a member of INITS Limited, a Nigerian company that helped set up the technical side of ReclaimNaija’s monitoring system.
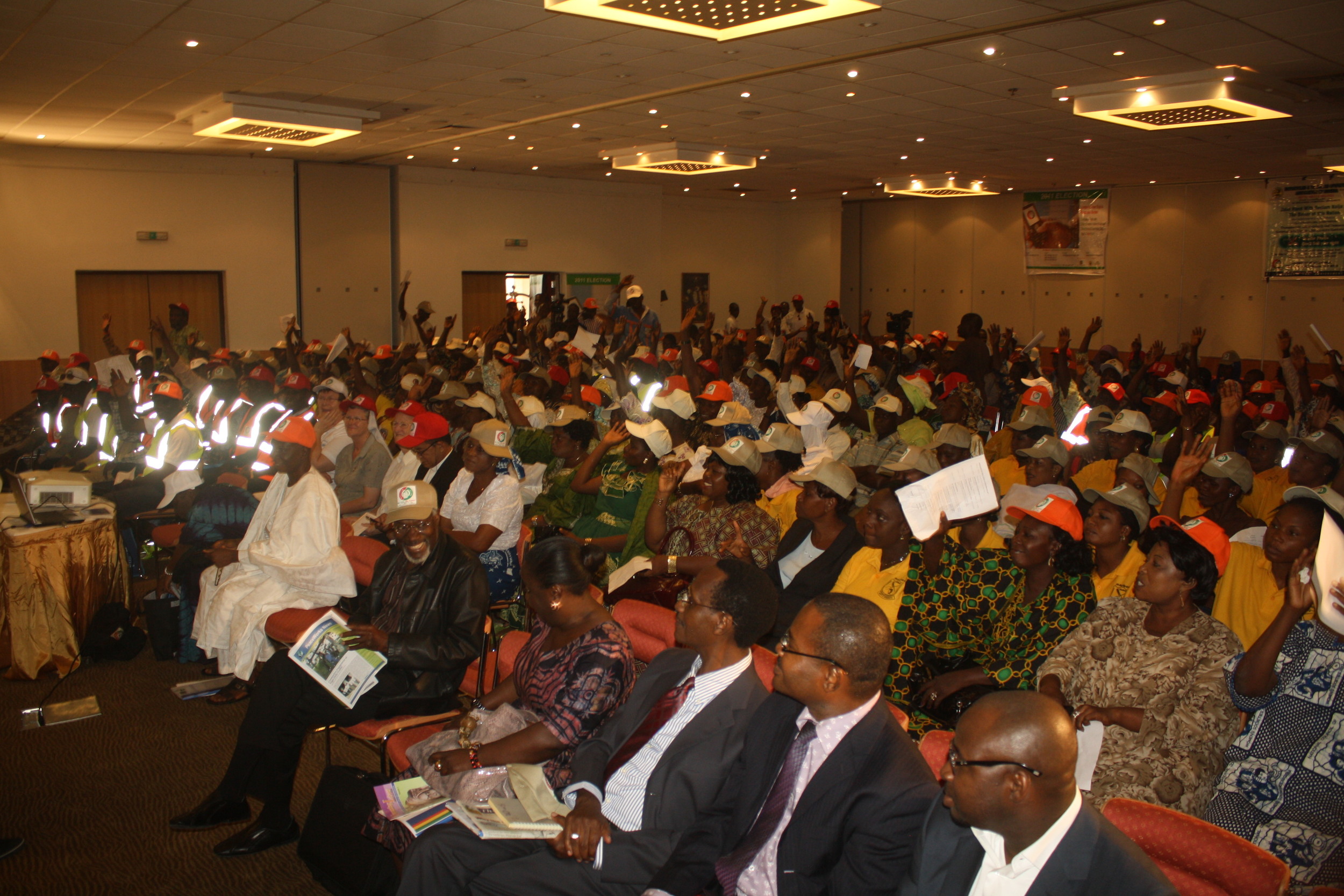

ReclaimNaija was established to “enhance the participation of grassroots people, organizations and local institutions in promoting electoral transparency, accountability and democratic governance in Nigeria” Ngozi Iwere tells me. ReclaimNaija achieved this participation in large part through voter education forums for community and grassroots leaders spread across the 36 States of the country and the Federal Capital Territory. As Ngozi explains “engaging the leaders of community-based social networks ensured that information got across to a large segment of society, as we trained leaders to pass on the message to their membership and constituencies.” Thus popular participation has been central to ReclaimNaija’s monitoring platform.During the January 2011 Voters Registration Exercise, ReclaimNaija received 15,000 reports from the public over two weeks. It is important “to have an election monitoring service that aids troubleshooting to expose and document fraud” says Ngozi Iwere. The election registration process proved this; on receiving messages about problems such as lack of registration cards ReclaimNaija was often able to communicate with the electoral body, thus helping improve the efficiency of the registration process.
Providing the option to make election reports via text message has improved the scope of ReclaimNaija’s work, helping them to target grassroots communities more effectively. “It is very important to have an election monitoring service that utilises tools that the average citizen is very familiar with” says Ngozi, explaining ReclaimNaija’s choice to provide the option for citizens to make reports via mobile phone.

Reflecting on the penetration levels that have made SMS such a powerful communications platform, Ngozi adds, “According to the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC), Nigeria has 83 million active GSM lines.” Although the platform offered citizens other means of reporting, such as email, voice calls, Twitter, Facebook and direct reporting on the website, Ngozi explains they’ve found that “SMS was the most utilised medium both during the voter registration exercise and the aborted National Assembly Elections on Saturday 2nd April.”
The system clearly continues to be a powerful way for Nigerians to communicate throughout the recent date changes. The National Assembly elections, originally due on April 2nd 2011 were pushed back twice as a result of many problems, including lack of voting materials and staff absences at polling stations. The whole election process has now been re-scheduled. The National Assembly elections went ahead on 9th April, and they are due to be followed by the presidential poll on April 16th and the governorship election on April 26th. Confusion over the election dates left some Nigerians suspicious about the validity of the elections.
“There has been a lot of scepticism surrounding the 2011 elections, even more so with the recent postponement,” points out Nosarieme Garrick, a Nigerian who has made use of the ReclaimNaija reporting system and also works for VoteorQuench.org, a social media effort to get young Nigerians engaged in the elections. Nosarieme has observed that some people are assuming that the problems are orchestrated attempts to facilitate rigging.
In line with this, one message received through ReclaimNaija during the first attempt at the National Assembly election said “more than half of registered voters here [in my voting station] couldn’t find their names… Is this an attempt to reduce the number of voters in Lagos?”
However, Nosarieme suggests that having a service like ReclaimNaija has meant people are able to act on their concerns. “Reclaim Naija is allowing eyewitness accounts from average citizens to be collected on the actual happenings during elections, and people understand that their reports are not falling on deaf ears.” Furthermore, although Nigerians were unhappy at the postponement, there is also hope around improving the voting process. Nigerian Femi Taiwo explains “if shifting the date was what it was going to take to get it right this time around… then the postponement was the right thing to do.”
Citizens have been able to report a wide variety of issues – including electoral malpractices, corruption and incidences confusion and unrest. One would-be voter, for example, sent a message on the day National Assembly elections were due to start, stating, “here at Umudagu boot, no staff or material or any sign there will be election. Hundreds of voters are loitering without accreditation and it is 9.00am.”
These citizen reports have become a valuable source of information for the Independent National Electoral Commission (INEC), who are responsible for running the elections, thus representing the voice of the people to the authorities. ReclaimNaija collate reports and send directly on to the INEC in real time.
“If the INEC hadn’t seen these reports they would not have known about the level of problems being experienced by Nigerians; there would not have been this kind of proof” says Linda Kamau, an Ushahidi developer was in Nigeria to see the launch of ReclaimNaija system. There is clearly great power in ensuring the voices of the Nigerian people reach the authorities running the elections.
ReclaimNaija has been a great success so far, and in no small part due to the power of using SMS. As Ngozi Iwere explains, using mobile phones “puts the power of effective monitoring in the hands of the people.” Yet it is the Nigerian people themselves who are central to the process, and the technology is a facilitator for their participation. Ngozi makes clear “there is a deep yearning for change among the populace and citizens see this election as an opportunity to make that change happen.”