After successfully using FrontlineSMS in the Tomorrow is a New Day (TND) project to monitor and improve radio dramas in the Niger Delta, SFCG Nigeria chose to use the platform in a completely different capacity in Jos, a city in Northern Nigeria. SFCG Nigeria is part of Search for Common Ground, one of the first and largest conflict resolution focused NGOs.
FrontlineSMS transforms Community Radio in Malawi
Nkhotakota Community Radio Station, along Lake Malawi, is a Malawi Communication Regulatory Authority (MACRA) recognized broadcaster and has been in operation for eleven years. More than 500,000 people live within our coverage area- transmissions reach Nkhotakota and Ntchisi districts and parts of Nkhatabay, Salima, Dowa, Mzimbaand Kasungu.
Now Showing: Africa's Voices
Coming to you from the University of Cambridge's Centre of Governance and Human Rights, we are pleased to feature a short film about the Africa's Voices project. This research pilot project supported local radio stations to use FrontlineSMS for audience participation, in an effort to continue to enhance citizen-based dialogue. Radio is still the killer app in Africa for sharing information. Adding mobile turns a one-to-many medium into a two-way interactive opportunity, empowering people to ask questions and hold their leaders to account.
Combining Local Radio and Mobile Phones to Promote Climate Stewardship
According to the report, with support from the Foundation to Promote Open Society, Developing Radio Partners (DRP) launched the one year pilot project, working with three local radio stations in each country. The primary aim of Zachilengedwe Tsogolo Lathu, as the participants named it ("Our Environment, Our Future"), was to empower rural Zambians and Malawians to address key climate change issues, especially local deforestation, by improving their access to information on the subject via radio and mobile phones.
FIRST Response Radio - Life Saving Information in Disaster
A big thank you to Mike Adams, the INTL Coordinator, for sharing his experiences with FrontlineSMS and further schooling us on how radio can facilitate in saving lives! In times of disaster radio not only saves lives, it can also bring hope and critical information to the affected community. When the 2004 tsunami struck Banda Aceh, Indonesia, all the radio and TV stations went off air. Similarly, during the 2005 South Asian earthquake, the only radio station near the epicentre lost its tower and went off air. In times like these, people are in desperate need of news and information on how to get to safety and how to survive. However, the unfortunate trend seen recently is that when radio is so important, many times it goes off the air and does not come back until well after the emergency is over.
How radio can be a conversation (not a lecture) and a jukebox (not a playlist)
Airtime is an awesome piece of software, built by Sourcefabric, which lets radio stations take control of programming via the web. It includes a simple scheduling calendar, smart playlists and automated playout. To mark World Radio Day 2013, FrontlineSMS:Radio's Amy O'Donnell wrote a post for Sourcefabric's blog on how this scheduling tool can be complemented by channels including SMS to help to make radio interactive. A snippet of the post is republished below, or you can read the original post in full here.
Star FM in Zimbabwe ensure Young People are the Stars
As with other community radio models, the Star FM community owns, manages and determines the content for programs – and in this case it is a community of young people. It is important for Bulawayo Youth Broadcasting to encourage youth participation because, as Philani explained, “They are the future leaders. The youth are encouraged to participate as they know that these issues affect them directly.”
“I am Loy, You are Loy”: A multimedia edu-tainment initiative engaging Cambodian youth in civic responsibility
I’ve been volunteering with the FrontlineSMS:Radio project and recently had the pleasure of speaking with Colin Spurway of BBC Media Action, an organization which helps people around the world to harness the media to promote change in their communities. Colin is the Project Director of Loy9(pronounced ‘Loy Pram-booun’), a multimedia initiative in Cambodia geared towards encouraging youth participation in civic life through the use of a television series, phone-in radio shows, online discussions and roadshows. We had a great discussion about the significance of the Loy9 initiative in promoting youth engagement in civic society through mobile technology, as well as some of the challenges.
Low tech adaptations for a community communications system
For the past month, I’ve been in Sudan working to set up the information flows and tech that will support SUDIA’s Community Communications System. From the tech and information management perspective, SUDIA’s System is interesting because it adapts to a low tech environment by integrating SMS and radio, and processing information largely offline. The System collects and disseminates information useful to communities that live along the migratory routes in Blue Nile State. It focuses on information that communities themselves can use to make their livelihoods more sustainable and more peaceful. In other words, the System is not aimed at organizations (Government or non-Government) that can use information to provide services or design interventions. Rather, it is aimed at communities helping themselves, and provides information that is useful to community leaders in organizing local community responses to livelihood challenges.
FrontlineSMS case study featured in new Rockefeller Foundation report: Learning from experimentation
The Rockefeller Foundation recently launched a new website, Capacity to Innovate.org, which examines lessons from a number of organizations including Ushahidi and Internews, and encapsulates them in three short reports which are well worth a read. FrontlineSMS is featured in the 'Learning From Experimentation' report, available from the website. Here's an excerpt, but we really recommend the whole report as a very readable and thought-provoking set of examples.
FrontlineSMS at 7: Rite FM, Ghana
FrontlineSMS is coming up to 7 years old in October 2012 - seven years ago, our Founder Ken Banks made the first, prototype version available for download. We're celebrating this milestone by highlighting the people we work for - our wonderful users. That's you, folks. See a slideshow of our users showing off their work here.
To kick us off, our FrontlineSMS:Radio Project Manager, Amy O'Donnell, highlights one of the many radio stations using FrontlineSMS - Rite FM, in Ghana. You'll hear more from our team, including Ken, in the next four weeks, as we highlight more of the incredible work done by people using FrontlineSMS around the world.
Amy writes:
Rite 90.1 FM is a radio station in Ghana which focuses on agriculture and social development to inform and educate local farmers. They take the lead from their audience, using SMS, and make sure their shows are responsive and relevant to their community. This use case, for me, also shows how SMS participation empowers communities to seek information vital to their livelihoods.
The catchment area of Rite FM is diverse, with both rural and urban populations in the Eastern Region each having their own unique challenges, so it's important to make sure programming is participatory and responds to local needs. This is why presenters, including Ike Obufio (photo above) use FrontlineSMS to encourage listeners to share their farming experiences via SMS. The audience are invited to text in their opinion to polls on the major causes of food insecurity or add their voices to debates on industrialized farming techniques and genetically modified foods.
Using SMS allows Rite FM to dramatically increase the number of people who can contribute - there is high mobile penetration in Ghana and because SMS is digital there's virtually no limit to the number of votes in a poll, for example. One of the presenters, Asamoah, believes offering options in communication channels is very powerful. He says; “If you stick to only phone-in, you can’t progress. You can’t reach out to everybody." SMS also adds flexibility to incorporate free-form comments fluidly - as he points out: “Even when I’ve not gone on air, I can respond to you.”
You can get involved too:
Starting today, we're collecting photos of our users telling the world how they use FrontlineSMS. If you want to get in on the act, take a photo of yourself or your team holding a piece of paper or a whiteboard telling the world what you do with FrontlineSMS. For example: 'I monitor elections', 'I safeguard children' or 'I make art'. You can see a slideshow of the photos we've had so far on our Flickr page.
It doesn't matter what language it's in as long as it's legible and if possible you should be able to see from the photo where it was taken, so, if you can, get out of the office!
You can: - post to Twitter or Instagram with the hashtag #FrontlineSMSat7 - email the picture and we'll post them - post the picture on our Ning network and we'll post them - post them on Flickr or any other web service and let us know where they are
FrontlineSMS bring a free, innovative solution to African broadcasters
As TV and radio broadcast markets intensify across several liberalized African countries, broadcasters need to find solutions to create more interactive communication with their audiences and build loyalty among them. SMS is one of those. There are a few SMS management software available out there butFrontlineSMS, a rather discreet solution provider has already been in the front line to support several African broadcasters. Sylvain Beletre, Senior Analyst, Balacing Act talked to Amy O'Donnell, Project Manager at FrontlineSMS on how SMS can be a very powerful media tool.
Looking at recent audience surveys across the African market, it is obvious that local audience want local content. Indeed, radio and TV operators have responded by increasingly shifting from a one-way broadcast to media that reach audiences by integrating interaction with listeners into programming.
But the lack of communication with the audience and the lack of finances are often major barriers for broadcast organizations working in African countries. Not knowing exactly what people want to watch and listen and not being able to check facts on the field, broadcasters have to find alternative solutions to make their job easier if they want to avoid being eaten up by more powerful competitors. And if broadcasters do not know their audience's program needs, they lose market share together with potential advertisers' revenues.
To read more, please click here.
FrontlineSMS:Radio adds an Exciting Tool to the Mix at Rite FM, Ghana
Guest Post By Tully McLoughlin
By 6:30 in the morning Owuraku Asamoah is seated comfortably at the black microphone in the Rite FM studio in Ghana, headphones on, twin computer monitors glowing, a laptop by his side displaying his Facebook page, his cell phone gripped firmly in one hand. “And this is how we’ll start today’s edition of the Morning Ride, being produced by Nii Alarbi,” he begins. “Believe in your hearts that something wonderful is about to happen.”
Rite FM broadcasts on 90.1 FM and online at www.ritefmonline.org from the bustling, 20,000-resident town of Somanya in the Eastern Region of Ghana. It occupies a unique niche of the radio space here – a commercial station for agriculture and social development. It is not simply an outlet for agricultural extension, nor do its programs present the standard rigmarole of music, politics, and religion. The catchment area, which includes portions of the urban Greater Accra region and large swaths of rural area in the Eastern and Volta regions, symbolizes that dual-demographic challenge.
I’m volunteering my time at Rite FM. I met the director of the station through their close partnership with Farm Radio International, an NGO with whom I work. Farm Radio was started in the late 1970s by a Canadian agricultural broadcaster who saw the need for better farmer-focused radio in Africa. The organization has been supporting commercial, public, and community stations on the continent since then, and in 2007 undertook the 42-month “African Farm Radio Research Initiative” with the support of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. Rite FM was one of five Ghanaian stations in the project.
My phone buzzes on the table by my bed, waking me up. “Tully. Owuraku wants you to talk about the Africa’s Voices project on the Morning Show in one minute.” That’s Kofi Baah, called Granpaa, the show’s producer. It’s July 20th, 7 am. Asamoah is devoting today’s show to a discussion of food security in Ghana, inspired by this month’s question for the project. The Africa’s Voices project is being undertaken jointly by the teams at FrontlineSMS:Radio and the Centre of Governance and Human Rights at Cambridge University UK, and Asamoah is taking the opportunity to cover the issue.
The question asks: “According to you, which is the bigger threat to food security in your area?” The options are: climate change, land access, market access, and food prices. I explain that by texting in their opinion they stand to win a remote-control, solar-powered, two-in-one lantern radio. A perfect way for farmers, in the field and off the grid, to tune in, the station’s director had told me the day before.
Asamoah takes calls and guides the conversation as it drifts from a debate on industrialized farming techniques to genetically modified foods. He is a pro at making the programming interactive. Beyond his demeanor, he has a number of tools at his disposal. There are two phone-in lines; an additional four lines on the Freedom Fone, an Interactive Voice Response tool; and an all-network SMS short code provided by the SIIMA system of SMS GH, a SMS-solutions company in Ghana. In addition, Rite FM operates its own website. And of course there is the battery of social outlets: a Facebook and user profile (ritefm), and a twitter feed (@rite901fm), and various satellite websites for other Rite FM projects. Now, the introduction of FrontlineSMS:Radio as part of the trial adds another exciting tool to the mix.
The advantage of this arsenal is that listeners participate and hosts facilitate in the way they’re most comfortable. Callers pepper the Morning Show, which runs from 6:30 to 9am, and The Drive, which runs from 2 to 5:30pm. But for shorter programs like Time With the CEO, profiling senior executives of agricultural businesses to showcase models of success and affluence along the agricultural value chain, and Women in Agriculture, focusing on the role of women as wives, mothers, traders, and entrepreneurs, the host may not be seeking a spread of opinions.
SMS, and to some extent Facebook or Twitter, give the host the flexibility to incorporate certain comments fluidly. That means, Asamoah points out, “Even when I’ve not gone on air, I can respond to you.” For listeners, says Nii Alarbi, a reporter and broadcaster for the Rite FM news team, SMS may be the only way they will contribute. “It’s not everybody who will like to call in for other listeners to hear his or her voice.” On a good day, a producer might expect to receive 10 or so texts in a show.
Even when the number of outlets to interact with listeners feels overwhelming, Asamoah sees that running in the opposite direction isn’t an option. “If you stick to only phone-in, you can’t progress. You can’t reach out to everybody.” Alarbi, who also hosts Herbs & Spices and the Agricultural Forum, says the day he does a show without taking any input, he will think, “Maybe I did it to my satisfaction, but I left my listeners behind.”
To find out more about Cambridge University's Centre of Governance and Human Rights "Africa's Voices" project click here and to learn about other projects using SMS with radio, visit FrontlineSMS:Radio's website.
Interview with European Journalism Centre Magazine: Is FrontlineSMS:Radio Advancing Social Change in Africa?
Amy O’Donnell, Radio Project Manager at FrontlineSMS:Radio recently spoke to Alessandra Bajec from the European Journalism Centre Magazine about the way FrontlineSMS is used to facilitate dynamic conversations between radio stations and their listeners in Africa and beyond. By enabling the powerful combination of radio broadcasting with SMS, FrontlineSMS:Radio is empowering and engaging communities across the globe. Republished here with permission or you can read the original post here. By Alessandra Bajec
Q. How has FrontlineSMS technology influenced African media?
Exponential growth in use of mobile technology has meant that many African media outlets are interested in using this technology effectively. By downloading FrontlineSMS and plugging in a mobile phone or GSM modem to a computer, people can use SMS in more sophisticated and professional ways.
We are moving from having contributions fed via SMS into an individual’s phone to a more open way of integrating SMS into content. We’re also supporting citizen journalists with tools for digital news gathering.
In Zambia, for example, Breeze FM radio uses FrontlineSMS to communicate with journalists. After gathering news tips received from the general public, the radio station organizes the evidence, sends SMS to journalists who may be out in the field, encouraging them to verify the facts and report.
Q. What is innovative about the FrontlineSMS software plugin?
With Version 2 recently released, FrontlineSMS has a user-friendly interface making it easier to manage larger volumes of messages, and to customize the software to better meet user needs. Pending messages can be sorted in a more timely fashion.
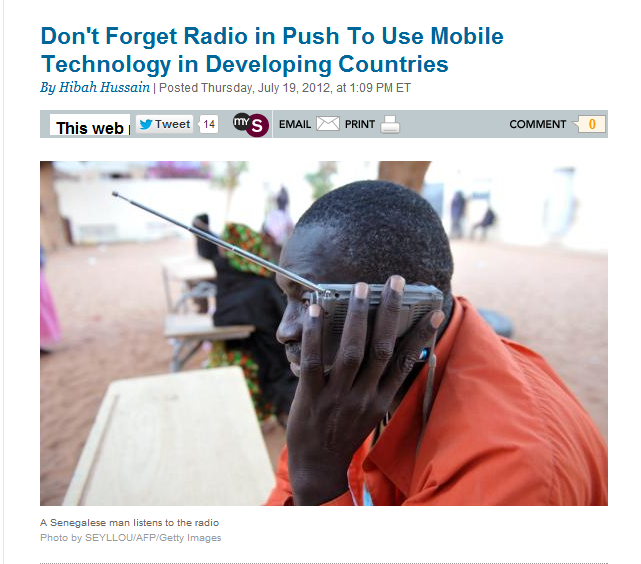
Slate.com features FrontlineSMS usage for a Radio station in Malawi
So radio is important—but not perfect. Although community radio stations often involve local residents in programming and long-term planning, getting real-time feedback from listeners can be challenging. Voice calls are expensive, and stations have a limited time to take calls from their audiences. This is where mobile telephony and text messaging can be a game changer, transforming radio listeners into active participants.Another example: FrontlineSMS, an organization devoted to leveraging mobile phones for development. Unlike similar organizations, Frontline has devoted significant resources to radio initiatives. Frontline’s platform has been used by community radio stations like Radio Mudzi Wathu in Malawi, which uses Frontline SMS to solicit questions, comments, and ideas from listeners. During prime listening hours, Radio Mudzi asks its audience questions like “why do you think that HIV/AIDS is increasing despite interventions?” and asks them to text their responses. They then aggregate the responses, analyze them, and take them to local policymakers and aid workers.
In addition to facilitating audience participation, SMS-oriented radio initiatives allow for unprecedented levels of audience research. After receiving feedback on any given issue, stations have a repository of information that they can analyze and look back on in order to better serve needs of audience. As they identify trends, needs, and concerns, radio stations can catalyze a profoundly fruitful cycle, using more relevant programming to drive audience engagement, thereby soliciting more feedback and dialogue.So how can we encourage more hybrid radio/mobile projects? First of all, we need to adjust the way we approach technology intended for the developing world. When designing, funding, researching, or discussing technology for development projects, we need to stop being fixated on one technology or platform and instead consider how new technology can be integrated with existing needs, values, and networks.